注意
點擊這裡下載完整的示例程式碼
神經網路¶
建立於:2017 年 3 月 24 日 | 最後更新:2024 年 5 月 6 日 | 最後驗證:2024 年 11 月 5 日
可以使用 torch.nn 套件構建神經網路。
現在您已經初步了解了 autograd,nn 依賴於 autograd 來定義模型並對其進行區分。nn.Module 包含層,以及一個返回 output 的 forward(input) 方法。
例如,看看這個對數字影像進行分類的網路
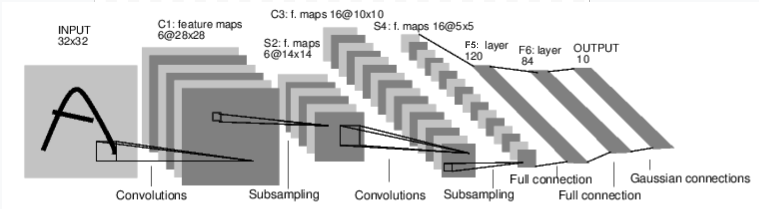
convnet¶
這是一個簡單的前饋網路。它獲取輸入,將其依次通過幾個層,然後最終給出輸出。
神經網路的典型訓練過程如下
定義具有一些可學習參數(或權重)的神經網路
迭代輸入的數據集
通過網路處理輸入
計算損失(輸出與正確答案的差距有多大)
將梯度反向傳播到網路的參數中
更新網路的權重,通常使用一個簡單的更新規則:
weight = weight - learning_rate * gradient
定義網路¶
讓我們定義這個網路
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
# 1 input image channel, 6 output channels, 5x5 square convolution
# kernel
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
# an affine operation: y = Wx + b
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120) # 5*5 from image dimension
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, input):
# Convolution layer C1: 1 input image channel, 6 output channels,
# 5x5 square convolution, it uses RELU activation function, and
# outputs a Tensor with size (N, 6, 28, 28), where N is the size of the batch
c1 = F.relu(self.conv1(input))
# Subsampling layer S2: 2x2 grid, purely functional,
# this layer does not have any parameter, and outputs a (N, 6, 14, 14) Tensor
s2 = F.max_pool2d(c1, (2, 2))
# Convolution layer C3: 6 input channels, 16 output channels,
# 5x5 square convolution, it uses RELU activation function, and
# outputs a (N, 16, 10, 10) Tensor
c3 = F.relu(self.conv2(s2))
# Subsampling layer S4: 2x2 grid, purely functional,
# this layer does not have any parameter, and outputs a (N, 16, 5, 5) Tensor
s4 = F.max_pool2d(c3, 2)
# Flatten operation: purely functional, outputs a (N, 400) Tensor
s4 = torch.flatten(s4, 1)
# Fully connected layer F5: (N, 400) Tensor input,
# and outputs a (N, 120) Tensor, it uses RELU activation function
f5 = F.relu(self.fc1(s4))
# Fully connected layer F6: (N, 120) Tensor input,
# and outputs a (N, 84) Tensor, it uses RELU activation function
f6 = F.relu(self.fc2(f5))
# Gaussian layer OUTPUT: (N, 84) Tensor input, and
# outputs a (N, 10) Tensor
output = self.fc3(f6)
return output
net = Net()
print(net)
Net(
(conv1): Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(conv2): Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(fc1): Linear(in_features=400, out_features=120, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84, bias=True)
(fc3): Linear(in_features=84, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
您只需要定義 forward 函數,並且 backward 函數(計算梯度的地方)會使用 autograd 自動為您定義。您可以在 forward 函數中使用任何 Tensor 運算。
模型的學習參數由 net.parameters() 返回
params = list(net.parameters())
print(len(params))
print(params[0].size()) # conv1's .weight
10
torch.Size([6, 1, 5, 5])
讓我們嘗試一個隨機的 32x32 輸入。注意:此網路 (LeNet) 的預期輸入大小為 32x32。要在 MNIST 數據集上使用此網路,請將數據集中的影像調整大小為 32x32。
input = torch.randn(1, 1, 32, 32)
out = net(input)
print(out)
tensor([[ 0.1453, -0.0590, -0.0065, 0.0905, 0.0146, -0.0805, -0.1211, -0.0394,
-0.0181, -0.0136]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>)
使用隨機梯度將所有參數的梯度緩衝區歸零並進行反向傳播
net.zero_grad()
out.backward(torch.randn(1, 10))
注意
torch.nn 僅支援小批量。整個 torch.nn 套件僅支援作為樣本小批量的輸入,而不是單個樣本。
例如,nn.Conv2d 將接收 nSamples x nChannels x Height x Width 的 4D Tensor。
如果您只有一個樣本,只需使用 input.unsqueeze(0) 添加一個假的批次維度。
在繼續之前,讓我們回顧一下到目前為止您所看到的所有類別。
- 回顧
torch.Tensor- 一個多維陣列,支援像backward()這樣的自動微分運算。也保持著梯度 w.r.t. 張量。nn.Module- 神經網路模組。封裝參數的便捷方法,帶有將它們移動到 GPU、匯出、加載等的輔助函數。nn.Parameter- 一種類型的 Tensor,當分配為Module的屬性時,會自動註冊為參數。autograd.Function- 實作 *autograd 運算的 forward 和 backward 定義*。每個Tensor運算都會建立至少一個Function節點,該節點連接到建立Tensor的函數,並*編碼其歷史記錄*。
- 到目前為止,我們已經涵蓋了
定義神經網路
處理輸入並呼叫 backward
- 還剩下
計算 loss
更新網路的權重
Loss Function¶
Loss function 接受一對 (output, target) 輸入,並計算一個值來估計 output 與 target 之間的差距。
在 nn 套件下有幾種不同的 loss functions。一個簡單的 loss function 是:nn.MSELoss,它計算 output 和 target 之間的均方誤差。
例如
tensor(1.3619, grad_fn=<MseLossBackward0>)
現在,如果您沿著 backward 方向追蹤 loss,使用其 .grad_fn 屬性,您將看到一個類似於以下的計算圖
input -> conv2d -> relu -> maxpool2d -> conv2d -> relu -> maxpool2d
-> flatten -> linear -> relu -> linear -> relu -> linear
-> MSELoss
-> loss
因此,當我們呼叫 loss.backward() 時,整個圖會針對神經網路參數進行微分,並且圖中所有具有 requires_grad=True 的 Tensors 都會將它們的 .grad Tensor 累加梯度。
為了說明,讓我們向後追蹤幾個步驟
<MseLossBackward0 object at 0x7f428dcaf520>
<AddmmBackward0 object at 0x7f428dcaf580>
<AccumulateGrad object at 0x7f428dcad510>
Backprop¶
要反向傳播誤差,我們只需要執行 loss.backward()。 您需要清除現有的梯度,否則梯度將會被累積到現有梯度中。
現在我們將呼叫 loss.backward(),並查看 backward 之前和之後 conv1 的 bias 梯度。
net.zero_grad() # zeroes the gradient buffers of all parameters
print('conv1.bias.grad before backward')
print(net.conv1.bias.grad)
loss.backward()
print('conv1.bias.grad after backward')
print(net.conv1.bias.grad)
conv1.bias.grad before backward
None
conv1.bias.grad after backward
tensor([ 0.0081, -0.0080, -0.0039, 0.0150, 0.0003, -0.0105])
現在,我們已經了解如何使用 loss functions。
稍後閱讀
神經網路套件包含各種模組和 loss functions,這些模組和 loss functions 構成了深度神經網路的構建模組。 完整的清單和文件位於 這裡。
唯一剩下要學習的是
更新網路的權重
更新權重¶
實務中最簡單的更新規則是 Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD)
weight = weight - learning_rate * gradient
我們可以使用簡單的 Python 程式碼來實現這一點
learning_rate = 0.01
for f in net.parameters():
f.data.sub_(f.grad.data * learning_rate)
但是,當您使用神經網路時,您會想要使用各種不同的更新規則,例如 SGD、Nesterov-SGD、Adam、RMSProp 等。為了實現這一點,我們建立了一個小套件:torch.optim,它實現了所有這些方法。 使用它非常簡單
import torch.optim as optim
# create your optimizer
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01)
# in your training loop:
optimizer.zero_grad() # zero the gradient buffers
output = net(input)
loss = criterion(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step() # Does the update
注意
請注意如何使用 optimizer.zero_grad() 手動將梯度緩衝區設定為零。 這是因為梯度會如 Backprop 節中所述進行累積。
指令碼的總執行時間: ( 0 分鐘 0.036 秒)



